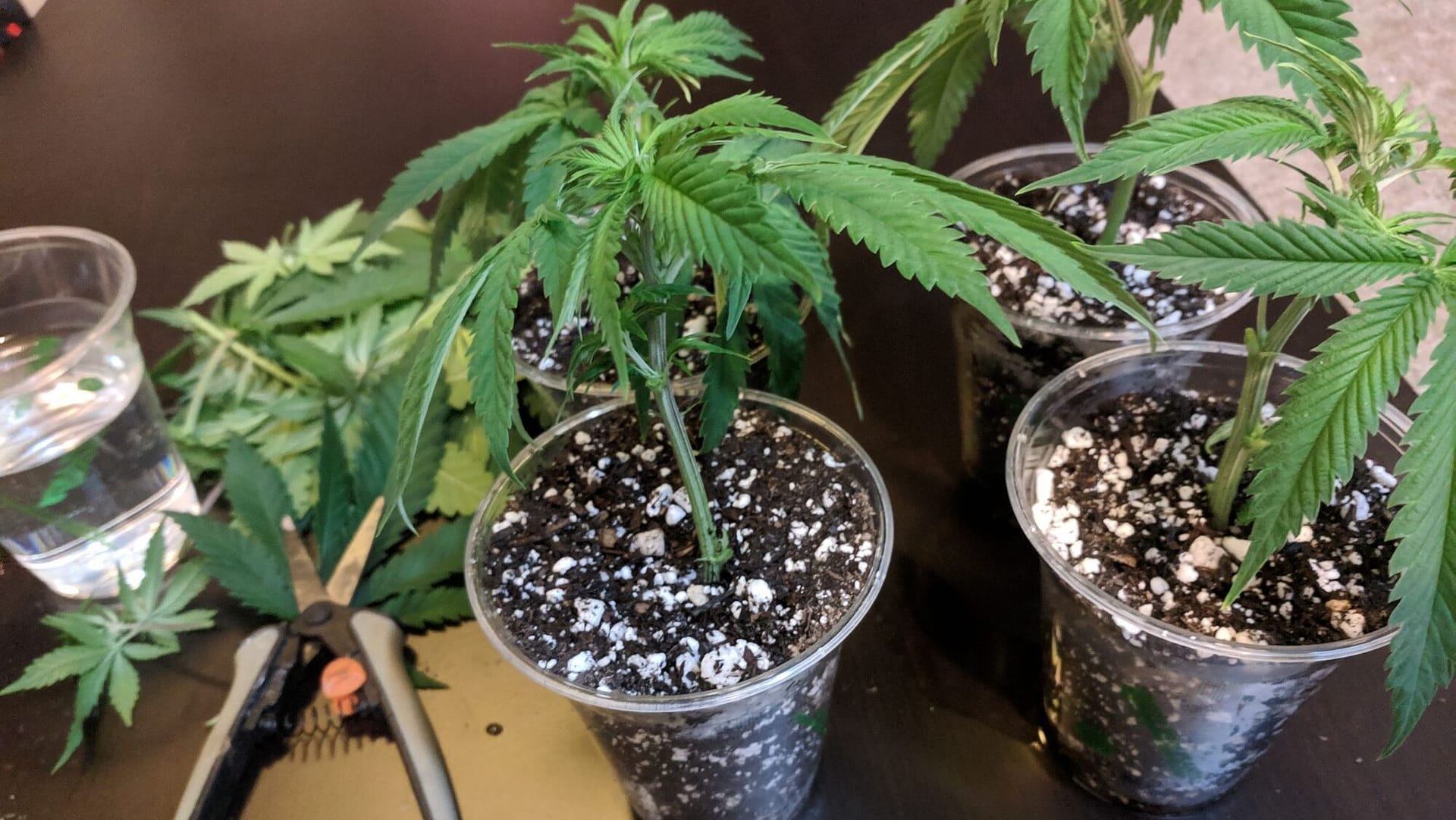
Cannabis cultivation is legal across Canada, leading to a surge in interest in different types of cannabis seeds, such as feminized cannabis seeds, regular cannabis seeds, and autoflower cannabis seeds.
Among these, autoflower cannabis plants have gained popularity due to their ability to flower automatically regardless of light cycles. However, many growers wonder if possible to clone autoflower cannabis plants in Canada and what the implications might be. Let us explore!
What Are Autoflower Cannabis Plants and Why Are They Popular in Canada?

Autoflower cannabis plants are a variety of cannabis that automatically transition from the vegetative stage to the flowering stage based on age rather than changes in light cycles. This characteristic distinguishes traditional photoperiod strains in specific light durations to initiate blooming. High CBD in autoflower cannabis plants refers to the genetic composition that yields elevated levels of cannabidiol, offering therapeutic benefits without inducing the psychoactive effects associated with THC.
Autoflower Cannabis Plants Advantages
- Autoflower plants have a quick growth cycle, typically maturing within 10-12 weeks from germination to harvest.
- Autoflowers tend to stay small in stature, making them ideal for indoor cultivation or discreet outdoor growing.
- These plants automatically transition from the vegetative stage to flowering, eliminating the need to manipulate light cycles.
- Autoflowers allow for multiple harvests in a single growing season, maximizing yield potential and providing a continuous supply of fresh buds.
However, they tend to be smaller and yield less compared to regular strains.
How Do Autoflower Cannabis Plants Grow in the Canadian Environment?
Autoflowering cannabis seeds stand out due to their unique genetics, combining traits from Ruderalis, Sativa, and Indica. They don’t rely on light cycles for flowering, instead switching to bloom automatically after a few weeks. This makes them ideal for beginners and discreet growing. Their rapid flowering is thanks to a protein called FT, which signals the plant to switch stages faster. Unlike traditional strains, autoflowers continue growing while flowering, allowing for various cultivation methods. However, they usually produce smaller plants and lower yields compared to photoperiod strains.
Here’s a breakdown of how they progress through different stages:
1. Germination
- Soak seeds in water for 24 hours.
- Transfer to moistened paper towels in a zip-lock bag.
- Use unscented, unbleached paper towels (pH 5.5-6.5).
- Wait for taproot emergence (1-2 days).
2. Seedling Stage
- Carefully transfer seedlings to suitable soil.
- Practice patience during emergence.
- Avoid overwatering and maintain proper pH.
3. Vegetative Stage (Weeks 1-6)
- True leaves develop.
- Provide mild nutrients and avoid overwatering.
- New leaves emerge as photosynthesis progresses.
- Consider training techniques for yield optimization (LST, Topping, FIMing).
- Use vegetative-stage nutrients, adjusting based on plant growth.
4. Pre-Flowering/Flowering Stage (Weeks 7-9)
- Buds begin to swell.
- Transition to full-strength flowering nutrients.
- Monitor plant health and continue nutrient application.
5. Harvesting Stage (Weeks 10-11)
- Stop nutrient application and flush with plain water.
- Buds mature and pistils may turn amber (harvest indicator).
- Use sterilized scissors and gloves for harvest.
- Adjust harvesting method based on environment and plant size.
6. Drying, Trimming, and Curing
- Dry buds in a controlled environment (7-14 days, 60-70°F, 55-65% humidity).
- Trim buds with dedicated scissors.
- Store in mason jars for curing.
Also Read: Cannabis Legalization in Canada – What you need to know
Understanding Cloning in Cannabis: Benefits, Risks, and Methods

Clone autoflower cannabis plants involves propagating genetically identical copies of autoflowering strains through a cloning process, preserving desirable traits. This method ensures the preservation of consistent strain characteristics, growth habits, and overall quality. A well-maintained and nurtured clone autoflower cannabis plants can thrive and exhibit robust health.
Many growers prefer cloning for its efficiency in replicating specific traits and avoiding genetic variability that can occur with seeds. Additionally, cloning allows cultivators to skip the germination phase, accelerating the growth process. In regions like Canada, where precise strain preferences and genetic stability are crucial for commercial and personal cultivation, cloning remains a popular practice among cannabis enthusiasts and commercial producers alike. Yet, cloning autoflower plants presents a challenge due to their distinct genetic composition and rapid flowering cycle, resulting in fewer successful attempts to clone autoflower cannabis plants.
Can We Clone Autoflower Cannabis Plants?
Cannabis plants, like many others, can be cloned by taking cuttings from a healthy mother plant to produce genetically identical offspring, preserving desired traits. However, cloning autoflower cannabis plants presents challenges due to their unique genetics and rapid flowering cycle, making successful attempts less common. Typically, clones are taken when the plant has 4-6 nodes and is in the vegetative stage with at least 18 hours of light. The cuttings are treated with rooting hormone, placed in soil, and covered with a dome for root development. While cloning is suitable for photoperiod strains, it’s less successful for autoflowering plants due to their accelerated flowering.
Pros of Cloning Cannabis Plants
- Cloning ensures that each new plant inherits the exact genetic traits of the mother plant, maintaining consistency in traits like potency, yield, and aroma, including when attempting to clone autoflower cannabis plants.
- Cloning skips the germination and vegetative growth stages, allowing growers to produce mature plants more quickly than from seeds, including clone autoflower cannabis plants.
- By eliminating the need to purchase new seeds, cloning can be a cost-effective method for expanding a cannabis garden.
- Cloning allows growers to preserve desirable traits from exceptional mother plants, ensuring the continuation of superior genetics, including when attempting to clone autoflower cannabis plants.
Cons of Cloning Cannabis Plants
- Cloned plants are genetically identical, making them susceptible to the same pests, diseases, and environmental stresses as the mother plant.
- Relying solely on cloning can limit genetic diversity within a cannabis garden, potentially making it more susceptible to catastrophic losses from pests or diseases.
- Cloned plants, including those from clone autoflower cannabis plants, may experience genetic degradation over successive generations, diminishing their vigor and yield.
Is It Possible To Clone Autoflower Cannabis Plants?
Autoflowers, unlike photoperiod strains, begin flowering on their schedule, typically within 3-4 weeks of growth. While it’s technically possible to clone autoflowers cannabis plants like other cannabis plants, it’s often unsuccessful due to their unique genetics. Autoflowers belong to the Ruderalis species, known for their rapid flowering and adaptation to harsh conditions. Unlike photoperiod strains that require 5-6 months to grow and flower, autoflowers complete their cycle in just 3 months or less. This speed is advantageous, allowing for quicker harvests, but it also makes cloning challenging. The genetic makeup of autoflowers results in difficulties with successful cloning attempts. Despite this, attempting to clone autoflower cannabis plants remains a challenge for growers.
Factors to Consider Before Cloning Autoflower Cannabis Plants

- Genetic Stability: Autoflower genetics may vary, impacting clone uniformity and growth characteristics.
- Growth Stage: Cloning success hinges on selecting healthy mother plants in the vegetative stage, typically 3-4 weeks after germination.
- Limited Timeframe: Autoflowers have a short lifecycle (10-12 weeks), providing a narrow window for successful cloning.
- Early Flowering: Autoflowers begin flowering automatically, often before clones can root and establish themselves.
- Resource Allocation: Cloning diverts energy from autoflower mother plants, potentially affecting overall yield and vigor.
- Genetic Variability: Clone autoflower cannabis plants may exhibit unexpected traits due to genetic instability, impacting quality and potency.
- Risk of Stress: Manipulating autoflowers for cloning can induce stress, leading to growth stunting or hermaphroditism.
- Alternative Methods: Consider alternative propagation methods like seed germination or buying clones from reliable sources.
- Environmental Conditions: Ensure optimal growing conditions, including temperature, humidity, and light, to maximize cloning success.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Evaluate the cost and effort of cloning versus purchasing seeds or clones from reputable suppliers.
Steps and Stages For Doing Cloning of Autoflower Cannabis Plants
If one still decides to proceed with cloning auto flowers, here are the steps involved:
- Choose a healthy, vigorous mother plant free from signs of disease or stress.
- Cut a stem section containing at least two nodes using clean shears sterilized with rubbing alcohol.
- Remove lower leaves to expose more surface area for root development.
- Place the cutting in water immediately to prevent air bubbles from forming inside the stem.
- Prepare a rooting medium, such as rock wool cubes soaked in a cloning solution.
- Insert the cutting into the prepared rooting medium, ensuring good contact between the stem and the medium.
- Keep humidity levels above 80% and maintain temperatures around 72°F – 77°F.
What happens if we clone Autoflower Cannabis Plants?
Cloning autoflower cannabis plants carries notable drawbacks primarily attributed to their abridged life cycles and altered growth dynamics, which can make successful attempts to clone autoflower cannabis plants less common. Some consequences include:
- Cloning autoflower cannabis plants is technically possible but often yields poor results.
- Autoflowers have a predetermined growth cycle that isn’t influenced by light schedules like photoperiod plants.
- Cloning involves taking cuttings from a mother plant and rooting them to grow into new plants.
- Autoflowers tend to have a limited vegetative stage before transitioning to flowering, leaving less time for clones to establish themselves.
- Cloned autoflowers cannabis plants often struggle to grow properly, resulting in stunted plants with reduced yields.
- Any stress or setbacks during the cloning process can significantly impact the plant’s growth and development.
Overall, while cloning autoflowers is possible, it’s generally not recommended due to the low success rate and potential for poor outcomes, especially when attempting to clone autoflower cannabis plants.
How do Cloning Photoperiod Strains differ from Autoflowers?

To understand how cloning Photoperiod Strains differs from Autoflowers, we first need to understand what photoperiod strain is. So, Photoperiod strains refer to cannabis plants whose flowering determines the light-dark cycle. Generally, shorter night periods (longer days) encourage vegetative growth, while longer nights (shorter days) trigger flowering.
Significant differences distinguish photoperiod and autoflower cloning approaches:
- Genetic Stability: Photoperiod strains have stable genetics, meaning their offspring tend to have consistent traits. This makes cloning photoperiod strains more reliable in terms of replicating desired characteristics. On the other hand, autos, which often contain Ruderalis genetics, can exhibit more variability in their traits, making cloning less predictable.
- Light Dependence: Photoperiod strains rely on changes in light cycles to trigger the transition from vegetative growth to flowering. Typically, growers switch the light cycle to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness to induce flowering in photoperiod plants. In contrast, autoflowering strains are not dependent on light cycles to flower. They automatically begin flowering after a certain amount of time, usually around 3-4 weeks from germination. This reduced dependence on specific light conditions simplifies the cloning process for autoflowers, as growers don’t need to manipulate light cycles to induce flowering in the clones.
- Growth Rate and Timing: Photoperiod cannabis strains generally have longer vegetative phases compared to autoflowers. This longer vegetative phase provides more time for successful cloning, as the plants have more developed root systems and structural stability. Autoflowers, on the other hand, have a shorter vegetative phase and transition to flowering relatively quickly. This compressed timeline can make cloning autoflowers more challenging, as growers need to ensure successful rooting and establishment of clones before the plants enter the flowering stage.
- Stress Response: Photoperiod strains often exhibit better stress tolerance due to their stable genetics. Cloning photoperiod plants tends to result in less stress-related setbacks, such as stunted growth or reduced yields. In contrast, autoflowers may be more sensitive to stress during cloning, potentially leading to stunted growth, delayed flowering, or diminished yields.
In summary, while cloning photoperiod strains requires more precise light management and longer vegetative phases, autos offer a simpler cloning process but with less predictable outcomes due to their genetic variability.
Why shouldn’t you clone Autoflowers?
Here is why you should avoid cloning autoflowers:
- Reduced Yield Potential: As mentioned earlier, cloning reduces the overall yield potential of the mother plant.
- Short Lifespan: Typically, autoflower has a lifespan of 10-12 weeks from germination to harvest. By the time a cutting is taken and rooted, the original plant is already transitioning to flowering. This leaves little time for the clone to grow properly
- Increased Risk Of Hermaphroditism: Disrupting the natural growth pattern increases the likelihood of hermaphrodites appearing in your crop.
- Complexity: Navigating autoflower peculiarities demands advanced expertise, demanding proficient practitioners capable of managing nuanced variables.
- Expense: Specialized equipment required for nurturing autoflower clones adds extra costs, burdening budget-conscious enthusiasts.
What are the differences between growing cannabis clones as opposed to growing cannabis from seeds?
When deciding between cannabis clones versus cannabis seeds, there are several factors to consider. This comprehensive comparison reveals the following insights:
Cloning Cannabis Plant
- Genetics: Clones ensure genetic uniformity, maintaining consistent chemical profiles and physical characteristics.
- Time: Clones accelerate growth by bypassing germination stages, offering immediate vegetative development.
- Simplicity: Clones eliminate gender uncertainty and genetic variability, making them beginner-friendly.
- Space Efficiency: Cloning requires less space than seeding multiple plants simultaneously.
Growing Cannabis Plants from Seeds
- Genetics: Seeds provide genetic diversity, allowing experimentation with various strains and phenotypes.
- Adaptability: Seeds demonstrate better resilience to stressors, adapting more effectively to changing conditions.
- Health Maintenance: Seeds are free from inherited diseases, unlike clones vulnerable to pathogens from mother plants.
- Financial Considerations: Acquiring clones can be costly, while seeds offer a more economical option, especially from reputable suppliers.
Why does cloning generate fewer results in autoflower cannabis plants?
Clone autoflower cannabis plants generate fewer results due to several factors. Firstly, the energy of the plant is diverted towards healing cut wounds rather than bud growth, resulting in reduced yields. Additionally, the shortened vegetative phase limits the overall growth period, further impacting the final yield. Cloning also disturbs natural hormonal balances, increasing the risk of hermaphroditism, which can damage potency and yield quality. Overall, clone autoflower cannabis plants typically leads to inferior results compared to growing from seeds.
Alternative Methods for Growing Autoflowers Plants Apart from Cloning
Maximizing results with autoflowering cannabis strains without the need for cloning is achievable through a perpetual harvest routine, offering a sustainable approach to cultivation while bypassing the complexities of cloning autoflower cannabis plants. This approach involves staggering germination so that plants can be harvested at regular intervals, ensuring a continuous supply of high-quality buds. By strategically timing germination, growers can maintain a perpetual cycle of cultivation, allowing for a steady stream of fresh harvests without relying on cloning. This method capitalizes on the quick lifecycle of autoflowers, making it easy to sustain a consistent supply of top-quality cannabis, including clone autoflower cannabis plants.
FAQs
Let’s discuss some popular questions and their solution for cloning Autoflower Cannabis Plants:
1. Does cloning affect the genetic consistency of auto-flowering cannabis?
Yes, cloning keeps the same genes as the original auto-flowering cannabis plant. But, there are problems like getting fewer buds, less time for growth, and smaller plants when you clone them.
2. What are the difficulties in cloning auto-flowering cannabis?
There are several troubles with cloning auto-flowers, like having less energy, a short time for growing, and a short life. Cloning doesn’t work as well as regular seed reproduction.
3. Is there any new technology in cloning auto-flowering cannabis?
Scientists and businesses are testing ways to make cloning easier and bigger using tissue culture methods, like turning cells into embryos or organs. Cannabis seed cultivation techniques may help with cloning tricky plants like auto-flowers.
4. How do the short growth and quick life of auto-flowering cannabis affect cloning choices and results?
Auto-flowering cannabis grows and lives quickly, which affects cloning decisions by setting strict deadlines and giving fewer buds. Cloning gets tough, needing expert help and creative answers.
Conclusion: Clone Or Not?
When deciding whether to clone autoflower cannabis plants, it’s crucial to weigh the facts. While cloning offers the advantage of replicating desired genetics, autoflowers often yield less due to their shorter growth cycle, posing a challenge for clones to fully develop before flowering. it’s essential to choose the right approach based on individual needs and preferences. Whether cloning or purchasing seeds, thorough research and consideration are key to a successful harvest.
Many growers opt to buy autoflower seeds from reputable online stores instead of cloning. This ensures access to a diverse selection of high-quality seeds with unique benefits. By selecting the right seeds, growers can maximize yield potential and achieve consistent results without the challenges of cloning.
For the best Autoflower Cannabis seeds in Canada, visit FarmKing Seeds Store!